Earlier when people were thirsty, they had no other option other than digging a well. However with the population growth and urbanization, it was impractical to build wells to address each family’s need. Instead people created tanks where a huge volume of water could be stored. The stored water is supplied to the citizens of many towns and villages. This method has many visible advantages over the traditional way. All families don’t have to put an effort in digging wells for themselves, no need of time to maintain wells, and no dedicated and suitable place is required. An established and dedicated organization such as Water board does everything necessary to take water from a river, pump to a tank, purify and deliver to the end consumers. Consumers only pay for the volume of the water they consume which covers the overhead costs of the producer as well.

The above scenario is an analogy to the base concept of cloud computing. Earlier, when computing facilities or computer systems are required by an organization or an individual, they had to buy computers and the network infrastructure. In addition they had to buy licenses for necessary software and install them, allocate dedicated space and employ necessary personnel to maintain the system. This requires a considerable initial setup cost and recurring maintenance cost. Scaling up and down based on market and business needs is not easy as it involves direct costs as well as management overheads associated with it. When the power of the internet was practically proven, the concept of cloud computing was emerged. As the water is received via pipes, computing power is received via internet. Thus the cloud computing can be explained as “computing via internet”.
Flavors of cloud computing
Cloud computing comes in different flavors. Following will be discussed in this article.
- IAAS – Infrastructure As A Service
- SAAS – Software As A Service
- PAAS – Platform As A Service
IAAS – Infrastructure as a Service
Dedicated or shared computing infrastructure is provided with the basic features such as the OS and other domain specific features installed. Users see these services as virtual machines with comprehensive administrative powers or hosting service with limited administration capabilities. Amazon EC2 is the most popular IAAS provider providing virtual computing power in the cloud. There are thousands of web hosting service providers such as godaddy.com, hostgater.com, ixwebhosting.com.
For instance let’s consider Amazon EC2. After creating an account in Amazon EC2, users can create virtual machines with his preferred OS, disk size, virtual memory size, firewall etc. Thereafter we can access those machines just as we access normal physical machines in a remote location. We can stop or terminate the machines when we are done with it or restart later when we need them again. In addition a snapshot of the machine can be created at any point so we can boot up another machines from the same state later. Following is a screenshot of the management console of EC2.
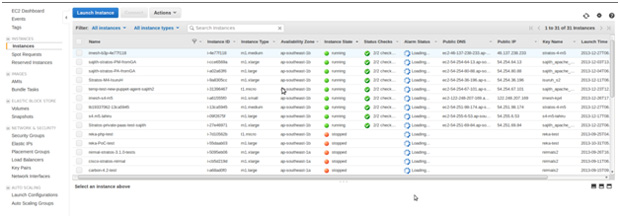
There are more services such as load balancing, scaling up and down etc. based on the user needs. Users are charged according to the resources they consumed such as virtual memory, storage and the time the machines were active. Another advantage of having an IAAS is we can scale up the system instantly. We can add and remove more hard disk space, memory or machines themselves or database instances easily; no ordering, no deployment, no baseline etc. Just play without even plugging. Coolest thing is that resources can be added in rush hours and removed when things go dull. Dynamic resource management to its max! These systems also support automatic scaling up and scaling down so application developers don’t have to think of typical constraints of the shared computer architecture.
SAAS – Software as a Service
Adding another layer on top of the computing infrastructure, users are given a valuable service through a single piece of software or a collection of software. Google’s collection of SAAS is the most famous free services stack among the general public. Gmail and Google Docs are the popular example applications for free SAASs. Even this article itself was started in the clouds as a Google Doc first – in favor of cloud computing. There are thousands of other paid services which provides services like online time management systems, online POS systems etc. Paid services charge in different ways like per year, per user and PAYG. PAYG or pay as you go is the cost model that charge for the resources (computing power, storage etc.) consumed. Users have the freedom to choose the cost model that best suits them. So you might question how free services generate revenue. The answer is it depends. Let’s consider Gmail as an example. Their main revenue model is advertisements. Gmail has more than 500 millions of users which imply Gmail make more than 5 billion advertisements display if we assume one average user sees 10 advertisements a day. Although it is impossible to assume how much they make for a year, but it should be a plenty. Additionally Google offers only a limited email and document space. Normal users can live with that. However for large corporate users needs to pay for additional email and document space when they grow. For e.g. there are numerous organizations in Sri Lanka uses Google services by paying subscription fees.
PAAS – Platform as a Service
There are organizations that provide platforms to build applications in the cloud where other organizations can build software services and host them. PAAS facilitates building of custom applications using a bunch of software platforms. This includes facilitating all of the development, maintenance and retiring stages of a typical software lifecycle. WSO2 Stratos, WSO2 App Factory, Heruko, Redhat OpenShift are high standard PAAS vendors. Please read more about WSO2 App Factory in this introductory article by the same author.
As an example, WSO2 Stratos is a 100% open source, multi tenanted for private, public and hybrid cloud deployments. It provides a complete stack of middleware products as a service and also mediation, governance, security, gadgets, monitoring and more by using the capabilities of WSO2 products. Third party runtimes such as PHP, MySQL, and Tomcat etc. can be plugged in via a concept called cartridge. StratosLive is the Stratos version hosted by WSO2. It is free for anyone interested.
Cloud Features
Every service hosted in the Internet is not a cloud service. They have some common characteristics which qualifies a service as a cloud service which is listed below.
Multi tenancy
Single software is shared among multiple users or organizations called tenants. The system and the data are partitioned among tenants. Different tenants can have different configurations. But the software service provided should be the same with different features on or off based on costing model etc.
Auto Scaling
The system automatically scale up (spawn up serving instances) during the rush time and automatically scale down (kill additional services) during the free time.
Distributed
System supports multiple nodes/instances running concurrently in different machines in a network, ability to save and transfer the overall state to work as a single servicing entity is also an attractive feature.

Disadvantages of the cloud
As every coin has two sides, cloud computing also has some inherent disadvantages. Organizations which handle the confidential data such as government organizations, mission critical applications etc. may think twice before storing their information in a public cloud.
Though it seems to be cheaper at the beginning, cloud may be expensive in the long run. Another problem is organizations may have to tolerate cloud services providers downtimes and bugs which can hinder the overall quality of service. If you can remember recent service degradations of Outlook and Gmail, you know what I meant by that.
When looking at the current industry, more and more organizations tend to move to the cloud since organizations needs to get the competitive advantages by delivering their services or products early to the market. Almost all the popular companies like Microsoft, Amazon, eBay, IBM, eBay, Redhat etc. have stepped into the cloud. Big companies like Google are born due to the cloud computing, and all its services are available via cloud. Through cloud, companies can make their services available to the customer faster. Cloud native features help to build a more distributive, auto scaling services that that supports any number of users. Cloud let the companies to address more users. For instance Microsoft Office what was a desktop application became more collaborative and accessible when it reached the cloud as Office 365.
Cloud is a new computing model of the era to build the applications shortly. However moving to a cloud might be time consuming initially as information may have to be separated and treated differently based on the security needs.
The Future
Rise of cloud computing is remarkable as it has made great success for this short time period. Almost every person who uses a computer or modern mobile phone, benefit from the power of cloud. Google, Email, Facebook, Dropbox, Google Drive, Skydrive are few of the system an average person uses which uses the Cloud. According to a recent report by IBM states that the businesses that moved to use cloud have doubled the revenue compared to its non-cloud counterparts. According a survey, 75 % of the surveyed businesses uses the cloud and the global market for the cloud is $158.8 Billion by 2014 which is 126.5% growth compared to 2013. So it is clear that the past of cloud computing was bright, but the future of cloud computing will be even brighter and business will be forced to use it to survive in the industry.
References
http://pzf.fremantle.org/2010/05/cloud-native.html?view=timeslide
http://whatis.techtarget.com/definition/multi-tenancy
http://www.gxsblogs.com/radkoj/2008/03/multi-tenancy-absolutely-critical-to-software-as-a-service-saas.html
http://www.businessinsider.com/the-10-most-important-companies-in-cloud-computing-2012-4?op=1
Image credits : creatiwittyblog.com, insideout.com, rent-a-techie.com/